Getting Started
Prerequisites
To access the CityLab testbed you need:
- A JFed account from the IMEC User Authority. If you do not have one, you can request one here (make sure the fill in 'CityOfThings' as the project name).
- You must be a member of the 'CityOfThings' project.
Both the application for a jFed account as the membership request for the CityOfThings project must be approved. As longs as you did not get a confirmation email of both approvals, you are not ready to start using the testbed!
Get a JFed account
You must have an account at the IMEC user authority. If you do not have one, go to the IMEC User Authority website and sign up for one. While signing up, you can immediately also request to be a member of the CityOfThings project (written exactly like this).
Get the JFed software
You also need to have the JFed software installed on your computer. You can do this before or after you create your JFed account. Go to https://jfed.ilabt.imec.be and download the appropriate installer for your operating system. On that website, you can also find some documentation on how to use this software (e.g. regarding certificates).
Using the testbed for the first time
Create and activate your experiment using jFed
Follow these steps to activate your nodes using jFed:
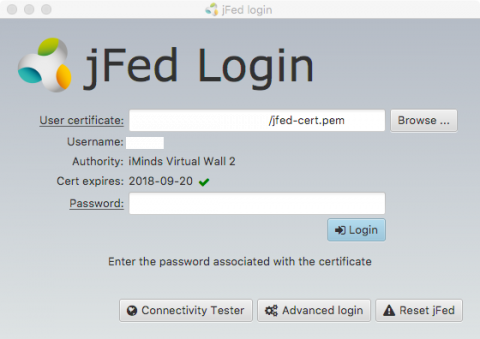
- Fire up jFed. If all goes well, you should be prompted to provide your User certificate and Password. Browse to the location where you stored the .pem-file (see jFed documentation regarding certificates), provide your password and click Login.
- If this is the first time you are using jFed to activate nodes in the imec CityLab testbed, you have to enable the proxy first. Click on Preferences, select the Proxy tab and click Run Proxy Test. Select the Always option for both Proxy for jFed and Proxy for SSH connections.
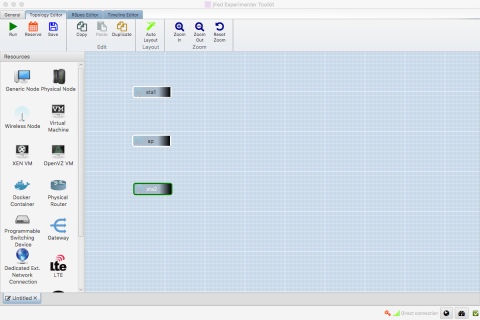
- Click on New
- Drag in 3 wireless nodes.
- Configure which nodes you want to use:
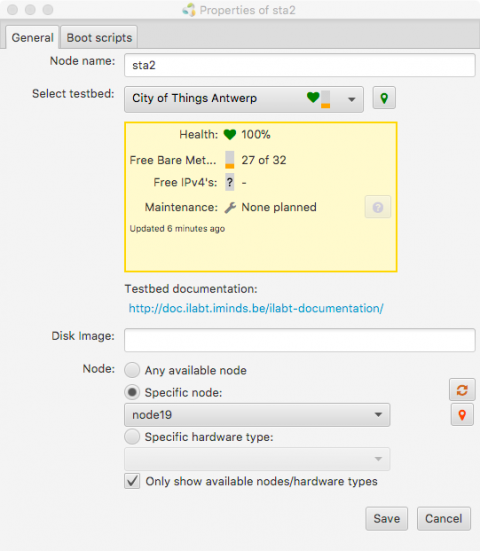
- Click the node, and select City of Things Antwerp. By default, WiLab2 is selected.
- Click on specific nodeand select a node there. Make sure you check on the map to select nodes that are in reach of each other! The CityLab nodes can be far away from each other, so if you don't pay attention, you will end up with an experiment that does not support wireless communication between the selected nodes! See using the node map for more information.
- Right click, Configure Node to change the properties (name/testbed/disk image/specific node).
- Name the three fixed nodes: ap and sta1 and sta2.
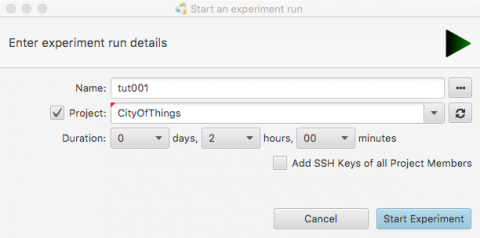
- Click Run to start your slice (Green arrow on the top left) and fill in a unique name for your slice.
- When all nodes turn green, your experiment is succesfully activated.
Configuration of Access Point
SSH to your AP node (double click it in jFed). Become root:
sudo su
Create a config file for the hostapd program:
nano /root/hostapd.conf
Add the following content to the config file:
interface=wlp1s0 driver=nl80211 country_code=BE ssid=demoX hw_mode=Z channel=Y
Replace X with a random number. Replace Y with your channel(1-11 for g, 36/40/44 for a) and Z with the WiFi mode (a or g). Start hostapd. The above config will setup an AP on wlan0 using 802.11a or g, channel Y, with SSID demoX:
hostapd /root/hostapd.conf
Open a second ssh terminal and give an IP address to the wlp1s0 interface so we can test the connection to the clients (in the next steps). Be sure to replace X with your number:
sudo su; ifconfig wlp1s0 192.168.X.1/24
Configuration of stations
For each of the two stations, open a ssh terminal and become root:
sudo su
Put the wireless interface into managed mode and specify the SSID so it knows to which AP it should connect
iwconfig wlp1s0 mode managed iwconfig wlp1s0 essid demoX
Specify an IP address and bring up the interface:
ifconfig wlan0 192.168.X.Z/24 up
make sure Z is not 1 and is different on both stations. Now, check if you can ping from one station to the other.
Using the node map
Note: A full-screen version of the node map can be found here The node map is a city map of Antwerp where all CityLab nodes are marked. Every node is shown on the map by by a clickable pin. When you click on a pin, a small text balloon opens that contains a link that brings you to a web page with some more information on that node.
You can use the node map to search for nodes that are in each others vicinity in order to set up an experiment with nodes that can actually communicate with the technology you will use. Due to the scale of the CityLab testbed, not all nodes can directly communicate with each other.
Please not that, while on the map, nodes might appear to be in close proximity, they do not necessarily have wireless connectivity (e.g. because there are obstacles blocking the line-of-sight between them). This is also highly dependent on technology. To help you select which nodes might be suitable for your experiment, we created an overlay on the map that shows which nodes have a direct connection with each other. To view this overlay, first select a type of wireless link from the drop-down menu. Then, you can optionally set filters based on RSSI values or on reliability. When you click the update button, the overlay will appear.
The overlay consists of colour-coded lines that give a visual clue of how good or bad a certain wireless link is. The lines themselves are also clickable, showing you the details of the link conditions. Do note that these figures come from a specially designed experiment to measure the link conditions. As these link conditions are also affected by external factors, they might change. You can use this node map as a guide, but do not consider it to be absolute reality...